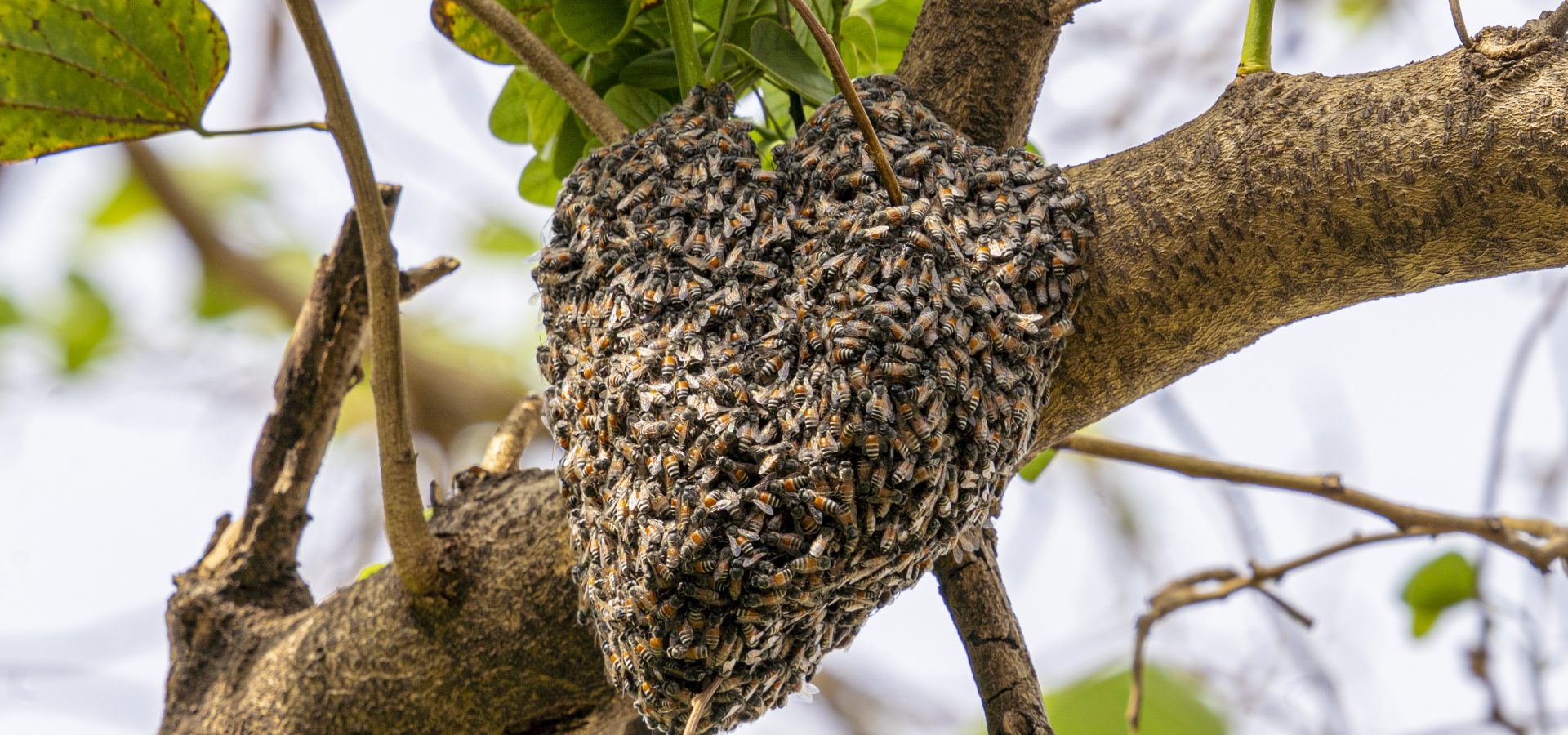
One of the most recognisable insects, Honey bees are small, yellow and black striped, winged creatures. Belonging to the order Hymenoptera, they are closely related to wasps, hornets, ants, and sawflies. They are often feared because of their painful stings.
Each year on 20th August, we celebrate World Honey Bee Day to remind ourselves of how significant these buzzing beauties are. It is well-known that Honey bees live in nests called honeycombs or hives. Here, we bring you some more fascinating facts about Honey bees!
Various Species of Honey Bees
Did you know that India is home to four native Honey bee species? Here they are!
- Indian Honey bee (Apis cerana indica) – Also known as the Asian Honey bee, they are frequently used in beekeeping for pollination.
- Giant rock bee (Apis dorsata) – The giant bees are the largest Honey bee species found in India, and are highly effective pollinators.
- Asian Dwarf bee (Apis florea) – The smallest of all indigenous bees, they are also known as the little bee.
- Stingless bee – Also known as dammer bees, they are able to penetrate flowers and extract honey with vitamins and minerals.

There’s another honey bee spotted in India which is the European Honey bee (Apis mellifera), and this is an introduced species (non-indegenous) that has gradually taken over the world. Due to its high efficiency of producing honey, it is widely used by beekeepers and farmers. This bee species fulfils India’s 75 percent of honey production.
Pollination of Plants
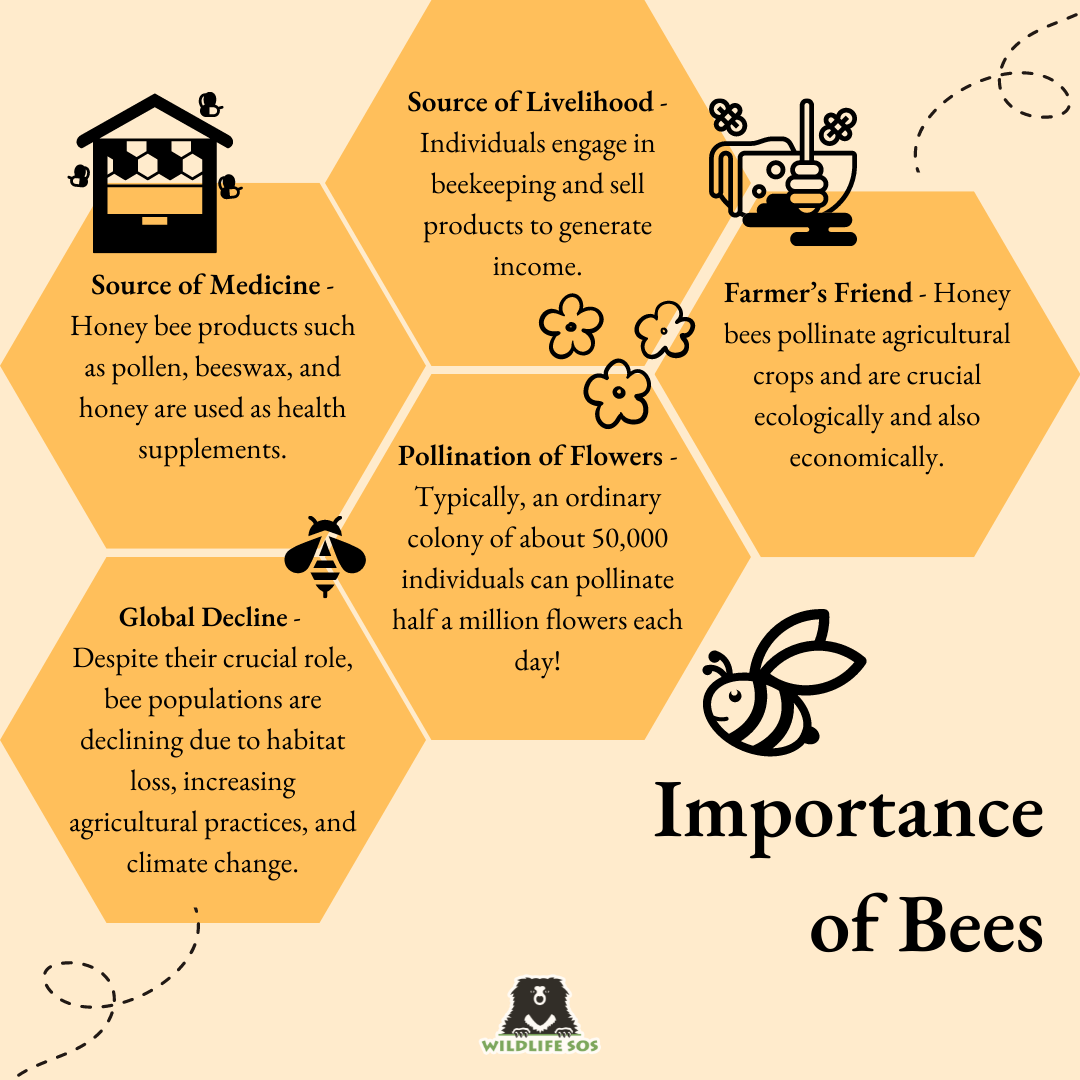
Flowering plants highly rely on pollinators, who carefully transfer pollen grains from one flower to another. Among the most efficient pollinating agents are Honey bees. Typically, an ordinary colony of about 50,000 individuals can pollinate half a million flowers each day! They hover from flower to flower to collect nectar and pollen, which they carry in a modified structure on their hind limbs called a “pollen basket”!
They pollinate not only wild plants, but also agricultural crops, thereby becoming farmers’ loyal companions! Honey bees are important not only ecologically, but also economically. Researchers have also attempted to calculate the economic value of Honey bee pollination to agricultural production, and it was found to be Rs. 3000 crores in India alone!
Complex Colony Structure
Honey bees are well known for their complex and highly organised colonies. A single colony may comprise 10,000 to 1,00,000 individuals. Each colony has three different types of individuals:
- Workers: About 60,000 bees are sexually immature females, who are responsible for numerous functions in the colony. They tend to the young ones, guard the entrance, build and clean honey combs, and collect all the necessary substances such as nectar, pollen, and water.
- Queen: Each colony has only one queen, who is capable of reproduction. With the sole purpose of egg laying, she’s fed on an exclusive diet of “royal jelly”.
- Drones: Drone bees are sexually developed male bees, each of whom has one (and only) aim in life: to mate with the queen bee. However, the act of mating is followed by an immediate death for them.
They Dance to Communicate!
A hive comprising thousands of bees requires excellent coordination amongst one another. Hence, Honey bees have devised an effective mode of communication: the “waggle dance”! Bees move with a vigour, angle, and for a specific duration to share information about the food source. This includes the direction, distance, quality, and identity of the food. As one worker bee goes on a lookout for a reliable source of nectar or pollen, it comes back to convey the details through this signature dance.
Hive Products
Hardwork and communication skills lead to the creation of intricate bee hives, where Honey bees store their very own bee-made products:
- Honey: It is produced from the nectar collected by Honey bees. Generally used as a sweetener and flavouring agent in food items and beverages, it is also a health supplement.
- Beeswax: It is secreted from glands situated on the bee’s abdomen. Commercially, this is used in the production of cosmetics, paints, and inks.
- Pollen: It is collected by bees in their “pollen baskets” from flowers, and this pollen is sometimes used as a health supplement.
- Propolis: The insects produce propolis or bee glue from balsams, resins, and sap derived from trees. Asian Dwarf bees are known to use this glue to keep away predatory ants. Bees even use it to seal any cracks in hives that they make in tree cavities.
- Royal jelly: Produced from the salivary glands of worker bees, it is royally fed to the queen bee.
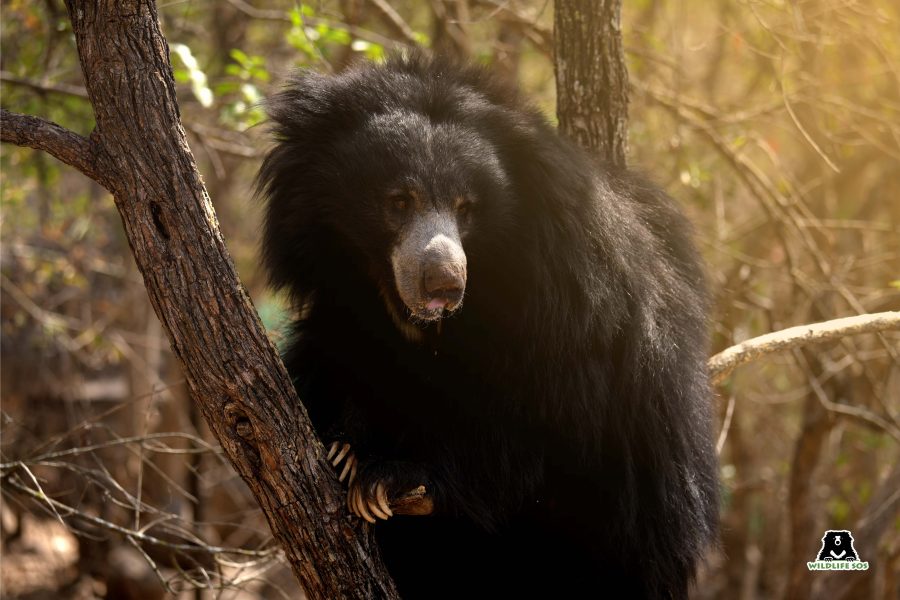
Honey Bees Serve Honey Bears!
Sloth bears are omnivorous creatures who feed on a wide array of items like termites and ants, fruits, flowers, seeds… but their love for honey is unmatched! Owing to their massive fondness for honey, the species is also known as the “honey bear”. Their scientific name is Melursus ursinus, which has been derived from Latin terms ‘mel’ meaning honey and ‘ursus’ meaning bear.
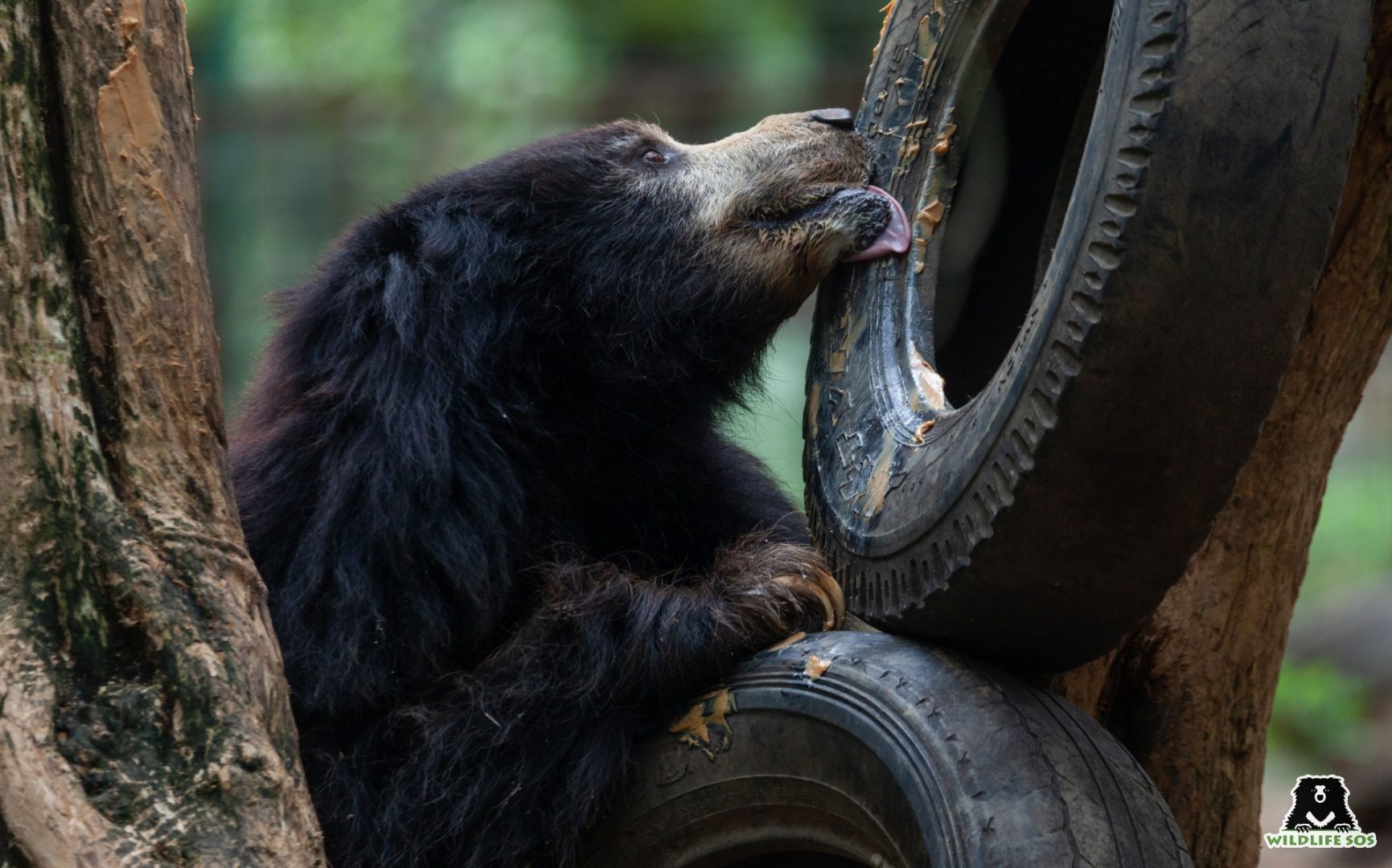

In the wild, Sloth bears are widely known to walk long distances to seek and forage on honey and bee larvae. They have been known to climb as high as 18 metres to bring down beehives! Mother bears even tear down and bring large honeycombs for their cubs to feed on, as they remain on the ground. Sometimes while relishing the sweet treats from the hive, the bears do not even mind being stung by bees!
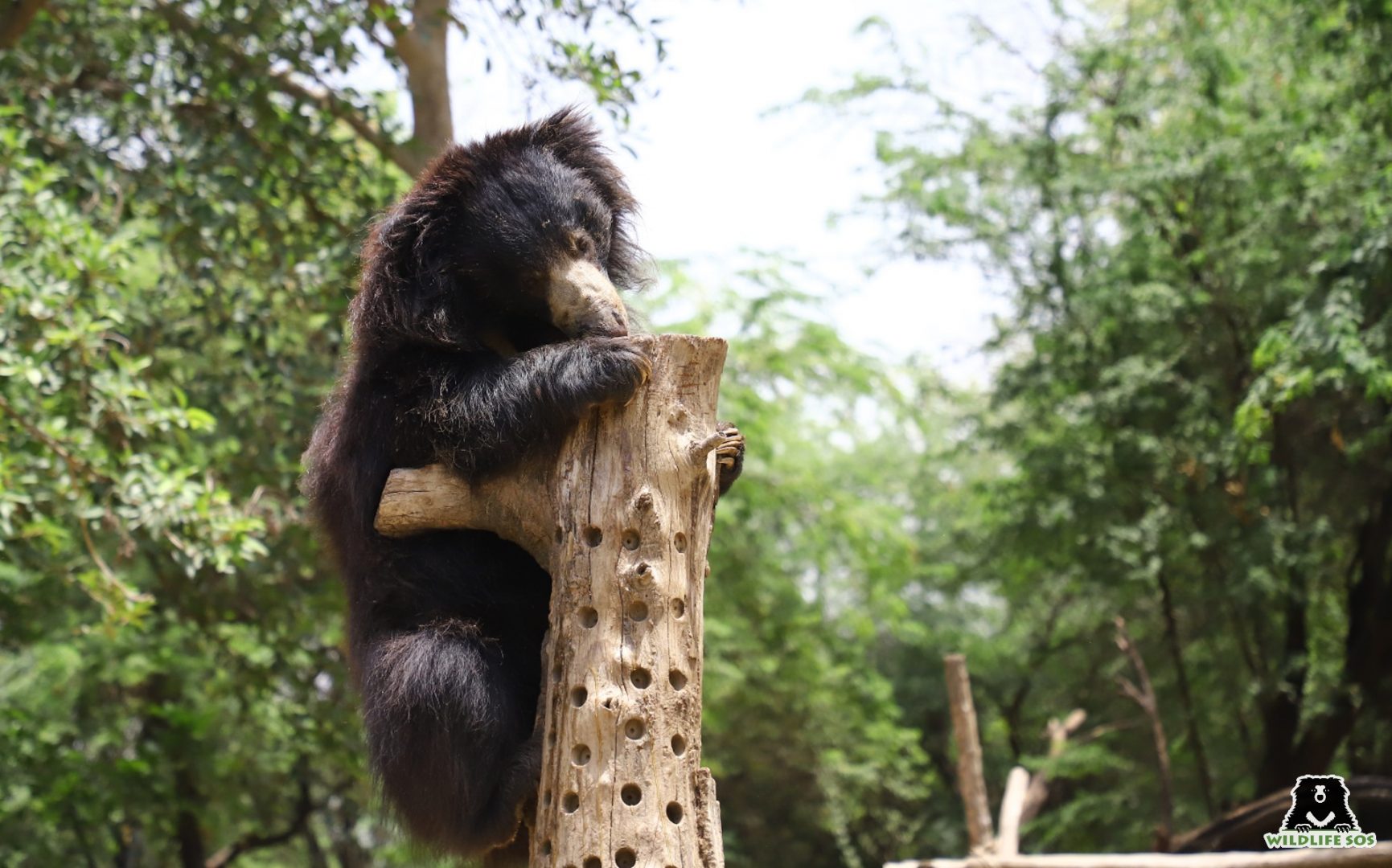
To satiate the hunger palette of Sloth bears that are under the care of Wildlife SOS, our team provides them with plenty of honey in their enrichments. They smear a generous amount of honey on wooden logs, enrichment balls, and other items which the bears enjoy relishing! You can donate to the care of our Sloth bears.

Bees Face an Unfortunate Decline
Considered as one of the most hard-working creatures on the planet, honey bees are crucial for food production, human livelihoods, and ecological balance. Their effective pollination helps nutritious plants to multiply. Over the recent decades, the global bee population is declining as a result of habitat loss, increasing agricultural practices, and climate change. It is therefore imperative to raise awareness on all species of bees, and how they can be safeguarded in a suitable environment.
For more interesting content on wildlife, subscribe to the Wildlife SOS newsletter now!





